Clin Res Cardiol (2021)
DOI DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-021-01843-w
|
|
Assessment of risk factors and outcome of device-related thrombosis in patients undergoing left atrial appendage occlusion – an analysis from the multicenter EUROC-DRT registry
|
|
V. O. Vij1, B. Al-Kassou1, S. Gloekler2, R. Galea2, M. Fürholz2, B. Meier2, M. Valgimigli2, G. O'Hara3, D. Arzamendi4, V. Agudelo4, X. Freixa5, E. Flores-Umanzor5, O. De Backer6, L. Sondergaard6, L. Nombela-Franco7, A. McInerney7, K. Korsholm8, J.-E. Nielsen-Kudsk8, S. S. Afzal9, T. Zeus9, F. K. Operhalski10, B. Schmidt11, G. Montalescot12, P. Guedeney12, X. Iriart13, M. Miton13, S. Saw14, T. Gilhofer15, L. Fauchier16, F. Meincke17, E. Veliqi17, N. Petri18, P. Nordbeck18, S. Rycerz19, D. Ognerubov20, E. Merkulow20, I. Cruz-Gonzalez21, R. González Ferreiro21, D. Bhatt22, A. Laricchia23, A. Mangieri23, H. Omran24, J. W. Schrickel1, J. Rodes-Cabau3, G. Nickenig1, A. Sedaghat1
|
|
1Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik II, Universitätsklinikum Bonn, Bonn; 2Inselspital - Universitätsspital Bern, Bern, CH; 3Quebec Heart & Lung Institute, Quebec City, Canada, CA; 4Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona, ES; 5Hospital Clinic Barcelona, Barcelona, ES; 6Rigshospitalet Copenhagen University Hospital, Copenhagen, DK; 7Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, ES; 8Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, DK; 9Klinik für Kardiologie, Pneumologie und Angiologie, Universitätsklinikum Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf; 10Medizinische Klinik I, Main-Kinzig-Kliniken GgmbH, Gelnhausen; 11CCB im AGAPLESION MARKUS KRANKENHAUS, Frankfurt am Main; 12Surbonne University Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital (AP-HP), Paris, FR; 13University Hospital Bordeaux, Bordeaux, FR; 14Vancouver General Hospital, Vancouver, CA; 15Kardiologie, Stadtspital Triemli Zürich, Zürich, CH; 16University Hospital Tours, Tours, FR; 17Kardiologie, Asklepios Klinik St. Georg, Hamburg; 18Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik I, Universitätsklinikum Würzburg, Würzburg; 19Klinik für Innere Medizin III: Kardiologie und Intensivmedizin, Schwarzwald-Baar Klinikum Villingen-Schwenningen GmbH, Villingen-Schwenningen; 20Russian Cardiology Research and Production Complex, Moscow, RU; 21University Hospital of Salamanca, Salamanca, ES; 22Harvard Medical School, Boston,, US; 23Maria Cecilia Hospital Cotignola, Cotignola, IT; 24Innere Medizin, St. Marien-Hospital, Bonn;
|
|
BACKGROUND
Left atrial appendage closure (LAAc) is a feasible alternative in stroke prevention, however device-related thrombosis (DRT) is a common complication that is paradoxically linked to an increased rate of adverse events. As DRT are still not well understood, we assessed risk factors and outcome in this multicenter approach from the EUROC-DRT registry.
METHODS AND RESULTS
Overall, 825 patients (149 with and 676 without DRT) were compared in order to assess risk factors for DRT formation as well as impact on outcome. Parameters included medical history, baseline and postprocedural echocardiographic characteristics and anticoagulation regime.
Patients with DRT formation were significantly older (76.2±8.5 vs. 74.5±9.1 years, p=0.029) and showed significantly higher incidences of prior stroke (54.4% vs. 36.0%, p<0.001) and non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (69.1% vs. 54.0%, p=0.001). Baseline echocardiography revealed a lower ejection fraction (52.8±10.6% vs. 54.6±11.8%, p=0.018) and left atrial appendage peak velocity (34.3±18.4 vs. 43.9±18.2 cm/s, p=0.001), as well as a higher incidence of spontaneous echocardiographic contrast (50.6% vs. 28.5%, p=0.001). Also, postprocedural dual antiplatelet therapy was less commonly initiated in patients with DRT (54.5% vs. 72.4%, p<0.001).
Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed a significantly increased incidence of stroke after LAAc in patients with DRT, however no difference in mortality (figure 1&2).
DISCUSSION
DRT formation is a common complication after LAAc and is associated with an increased stroke risk. As several risk factors were identified, postprocedural echocardiographic follow-ups should be performed regularly, in order to prevent adverse events linked to DRT formation. For this matter, a further optimization of oral anticoagulation regimes is warranted.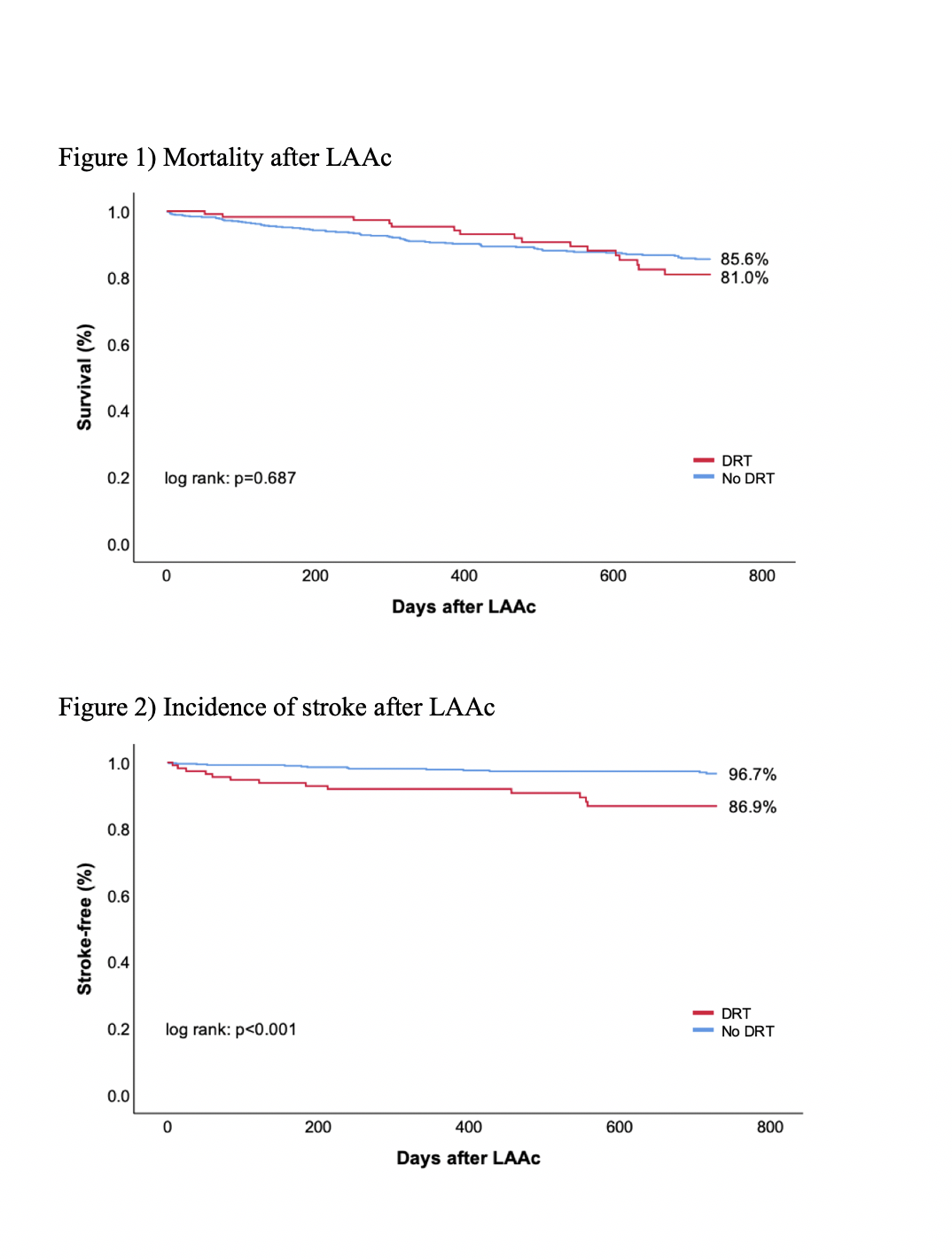
|
https://dgk.org/kongress_programme/jt2021/aP67.html
|